Clients receive a weekly email which gives some basic information about the status of their domain / website.
To the untrained eye, this might not mean much, so here’s some “eye training” 😉 …
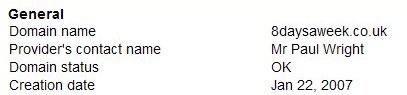
- your website domain (8daysaweek.co.uk in this example)
- my name as your provider
- Domain status “OK” means there are no issues with your account
- Creation date is when your website was set up on the server (this might not mean anything to you – lots of things can affect the date here, you don’t need to take note of it).
Although it may say “Unlimited” next to “Expiration date” (as in the example above), usually there will be a date here. It is the date that your current hosting agreement expires. Pay attention to this date, after which your website will go offline, unless another hosting agreement is in place.
![]()
This refers to whether you are controlling certain aspects of your domain yourself. If your domain is managed by me, then this will always say “Off”.

How much space on the server you have paid for. This is the space that you use for both your website, and any email stored on the server, especially if you use IMAP.
The “Size” number refers to how much of the space you’ve already used. In the example above there is still 62MB available.

Similar to size, this refers to the traffic, or bandwidth, allowed for your site each month. These figures are indirectly related to the size of your site, larger sites tend to need more bandwidth. However, really this figure is determined by the popularity of your site, and your use of email (and other services).
For instance, if you have a 1MB file on your website, available for others to download, and 9 people download it, you will use 1MB storage space, but 9MB of your traffic “allowance”.
If you send a 5MB email you’ll use another 5MB of your allowance, and so on.
Also bear in mind that large photos etc. affect this figure, so if your site has many images and lots of people browse the site, this will also use up bandwidth or “traffic”.
If you reach your “Traffic limit” your site will appear offline to visitors, so it’s worth keeping an eye on whether the traffic used is getting close to the limit.
![]()
An additional service to backup your website and emails (if stored on the server) is available on request. As you can see above, this customer isn’t paying for this service.
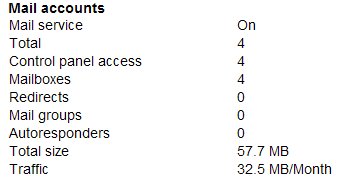
- Mail service – On
Shows that you are using the email service provided with your hosting package. This isn’t necessary if you have your own email server, or are using an external mail service, such as Google Apps. - Total, Control panel access, and Mailboxes, each refer to the total number of mailboxes activated on your domain. This is different to the number of email addresses, as a mailbox can have an unlimited number of email aliases (email mailboxes and aliases will be explained more fully in a future post).
- Redirects – this is a service where you can have an email address that will accept mail and forward it to another e-mail address.
- Mail groups – a mail group refers to an email address that will accept mail and forward it to multiple other email addresses (the mail group).
- Autoresponders – these can be set up to look for certain words or phrases in the subject or body of an email you receive and reply to the sender with a pre-prepared email message. They are often used to respond to regular information requests, for example if you invite your website visitors to “send an email to us@domain.com with the subject “brochure” to receive our latest brochure.
- Total size, Traffic – Similar to the Size and Traffic headings explained above, these numbers refer to the size and traffic used by your email service.
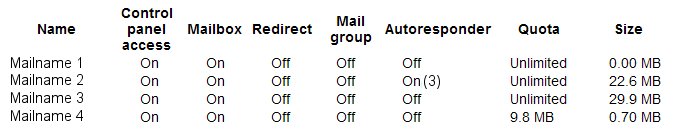
This is where you can see more detail about how your email service is set up and used.
In the example above, Mailname 1 accepts email, but actually this customer ‘pulls’ emails from this mailbox via POP3, so although they use traffic, there is no storage space taken up with mail to this address. The same effect could be achieved using a redirect, which would ‘push’ the emails, rather than them waiting to be collected.
Mailnames 2 & 3 are set up to store their email on the server. This means the emails can be accessed via webmail, or IMAP using any Internet enabled computer in the world. They have ‘Unlimited’ quotas meaning they can use all the available storage on the server, until there is no more room left. If they did, no one @that domain would receive email anymore, and the website would probably experience problems.
This is one reason why it’s a good idea to set quotas for individual mailboxes. Imagine a single, rarely used, ‘Unlimited’ mailbox started receiving lots of spam. Pretty soon the whole storage space would become filled with useless unsolicited email, causing problems for everyone.
Mailname 4 is a rarely used mailbox, which as you can see has a quota assigned. This means that if this user stored 9.8MB in their mailbox, even though this isn’t the limit of the entire domain storage, they would no longer receive emails (the emails would be returned to the sender with the message (mailbox full).



No user commented in " Domain Reports "
Follow-up comment rss or Leave a Trackback